
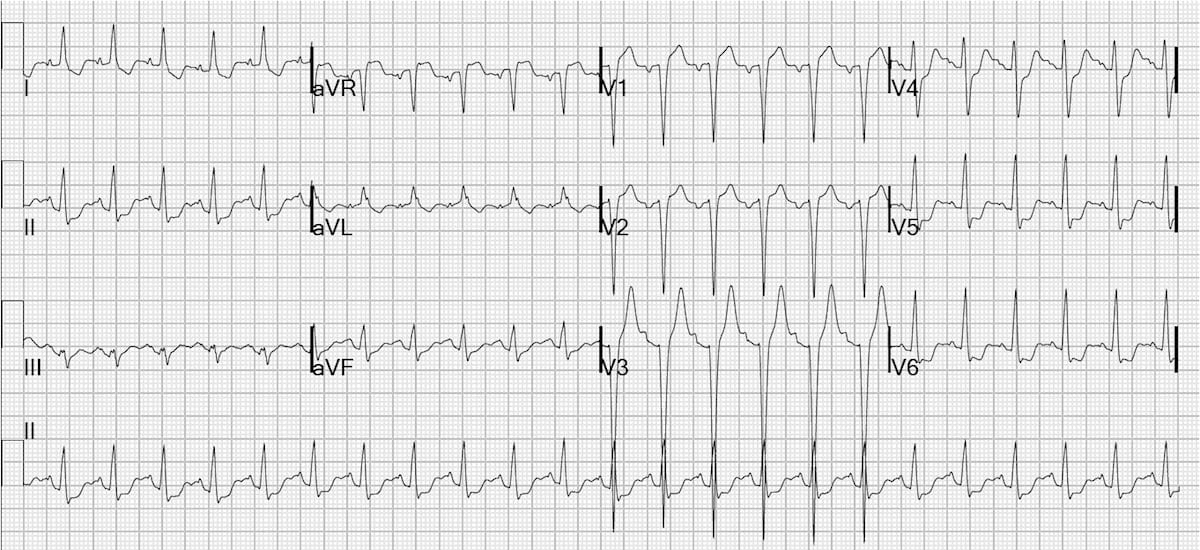
Ischemic Elevation of the ST segmentĮlevation of the ST segment in IHD is a highly probable sign of the pre-stage stage of the disease. The ST segment sometimes has a saddle-shaped configuration with funnel-like deformation of the chest. One method of investigation is an insufficient basis for diagnosing, therefore in disputable cases the patient is assigned other methods of diagnosis.
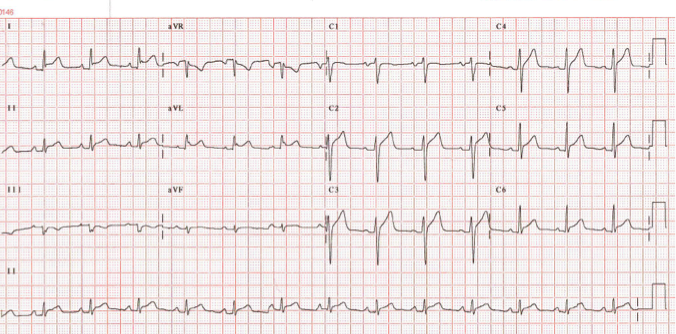
Nonspecific elevation of the ST segment on the ECG means that the curve is not quite standard, but within the physiological norm. Factors aggravating the course of myocardial infarction: age, low blood pressure, significant ischemia, manifested by abnormalities of the ST segment on the electrocardiogram, female or male gender (women die more often), kidney disease. Improving the methods of first aid has reduced the number of deaths. It is these hidden forms that are the cause of the high early mortality of people. There are painless forms of myocardial infarction. Clinical manifestations are always associated with the severity of ischemia. Measures to increase blood flow can save myocardium from necrosis. Elevation of ST - only one of its indirect features.Īcute coronary syndrome is a symptom complex that occurs when myocardial infarction is caused by a pronounced sharp decrease in coronary blood flow. The very first reason for ST segment elevation on an electrocardiogram is acute myocardial infarction. Similar changes are noted in viral myocarditis and resulting from staphylococcal or streptococcal angina. The myocyte membrane can also be damaged by pancreatic enzymes in acute pancreatitis, which is expressed by ST elevation on an electrocardiogram. The expressed hypotension causes an ischemia at patients with an ischemic heart disease. On the cardiogram in this case there are changes in the ST segment. Myocardial infarction is the death of cardiomyocytes caused by prolonged ischemia. Elevation of the ST segment is noted in the leads that are above the ischemic epicardium. The definition of leads in which ST segment elevation is present allows to localize the site of ischemia. In the case of subendocardial ischemia, the main potential is positive, and the ST segment shifts below the isoline. With transmural ischemia, a negative deviation is recorded, which becomes isoelectric only in the ST segment, leading to its elevation. ECG allows you to determine the extent of ischemia prevalence and what part of the heart it touched. Elevation of the ST segment and T wave is an early sign of myocardial ischemia.
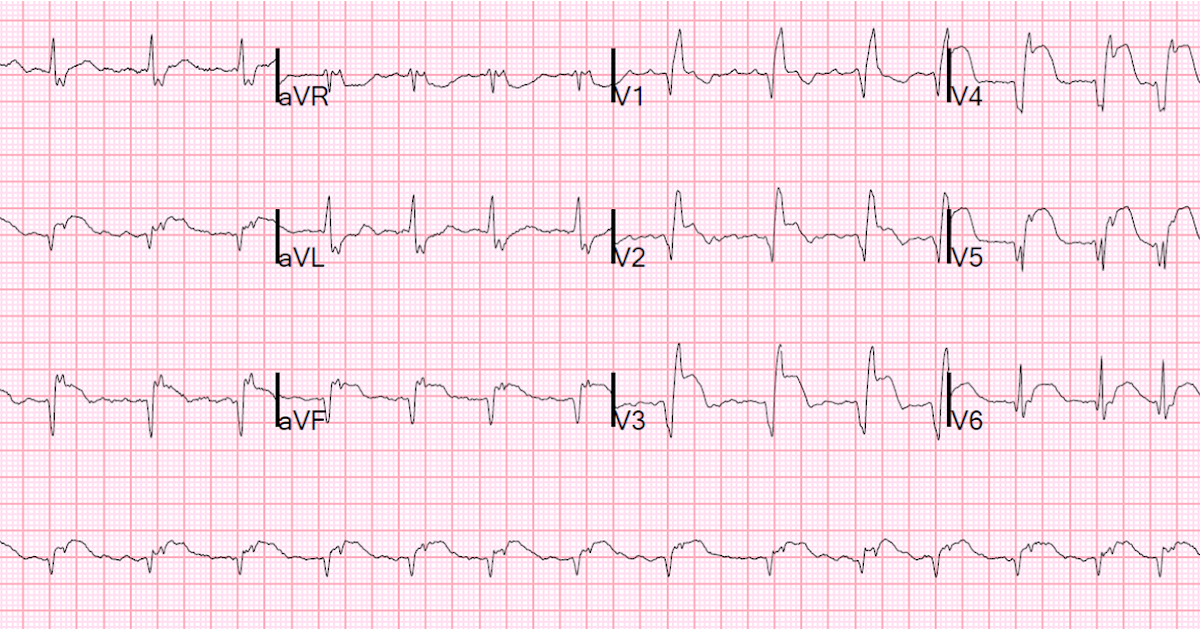
An electrocardiogram is the main method for diagnosing myocardial ischemia.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
